During this Covid-19 pandemic period, many people are working from home, and everybody needs to practise social distancing. It becomes a challenge for property agents to meet with each other and clients for documents exchange or signing.
Rather than to use the traditional (and tedious) “print, deliver by email, sign, return by post” sequence, PDF documents have the ability to provide a space for signing and offer an audit trail, together with the ability to “lock the document” after signing. These are useful to make the electronic signing process more widely acceptable in the business environment.
But First! Let’s stay updated with the legal requirements;
The Electronic Transactions Act (ETA)
The starting point is that the ETA provides for the legal recognition and use of electronic signatures and electronic records, thereby giving predictability and certainty to electronic transactions.
For electronic signatures, this effectively means that, where the conditions in the ETA are met, an electronic signature will satisfy any rule of law requiring a document or record to be signed – electronic signatures are given recognition as the functional equivalent of wet ink signatures.
Electronic Signatures: A workaround for issues arising from work-at-home measures by Dentons Rodyk, 05 March 2020

Using Electronic Signature for Real Estate Contracts
Section 6(d) of the Civil Law Act (Cap. 43), Sales and Purchase Agreements are required to be evidenced in writing and signed.

Formal real estate contracts require “wet-ink” signatures. These are also classified within “Excluded Matters” under the ETA as follows:
- The creation or execution of a will.
- Negotiable instruments, documents of title, bills of exchange, promissory notes, consignment notes, bills of lading, warehouse receipts or any transferable document or instrument that entitles the bearer or beneficiary to claim the delivery of goods or the payment of a sum of money.
- The creation, performance or enforcement of an indenture, a declaration of trust or power of attorney, with the exception of implied, constructive and resulting trusts.
- Any contract for the sale or other disposition of immovable property, or any interest in such property.
- The conveyance of immovable property or the transfer of any interest in immovable property.
Future of Electronic Transactions (legislation in Singapore)
There have been developments to promote the use of electronic (or digital) signatures. IMDA recently issued a consultation paper seeking views on taking some documents (OUT OF) the Excluded Matters. Meaning, this will allow such documents to be formally signed using electronic signatures.
Difference between Electronic Signature and Digital Signature
A quick illustration below to show the difference between Electronic (e-Signature) vs Digital Signature.
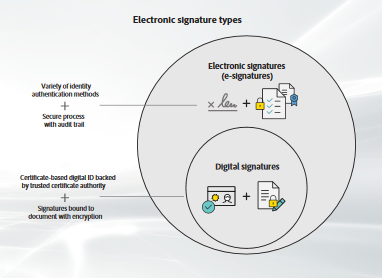
Electronic signatures (e-signatures) refer to any electronic process that indicates acceptance of an agreement or a record.
- A variety of common electronic authentication methods to verify signer identity, such as email, social IDs, passwords, or a phone PIN.
- Standard e-signatures use single factor authentication.
- Enhanced e-signatures use multifactor authentication to increase security when needed.
- Demonstrate proof of signing using a secure process that often includes an audit trail along with the final document.
Digital signatures use a specific method to sign documents electronically.
- Use a certificate-based digital ID to authenticate signer identity.
- Demonstrate proof of signing by binding each signature to the document with encryption — validation is done through trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs) or Trust Service Providers (TSPs).
Read more at https://acrobat.adobe.com/sea/en/sign/capabilities/digital-signatures-faq.html
In this recent article from Allen & Gledhill (Jun 2020), they have also offered to illustrate the differences between Digital Signatures (vs Electronic Signatures), mainly being that “digital signatures” seek to enhance security through the use of public key cryptography, as opposed to simply adding images of a signature through “cut-and-paste” or otherwise.
Within the article, it was also mentioned that Singapore is developing the National Digital Identity system (NDI) that will function as an extension of the existing SingPass authentication system.
This will definitely be very useful for verifying identity and implemented as a way to digitally “sign” or “endorse/agree” to a contract.
Create Your Own Digital Signature in less than 5 minutes
Online services that you can use to create PDF and sign documents electronically
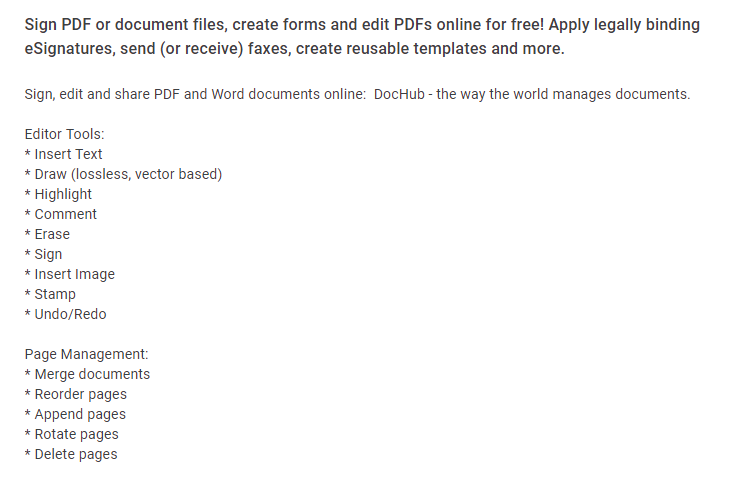
DOCHUB
One recommended method is is to use DocHub – it works very well with Google (GMAIL and GSUITE users). You can simply send documents from Google Drive or Gmail directly into Dochub for editing, signing, etc.
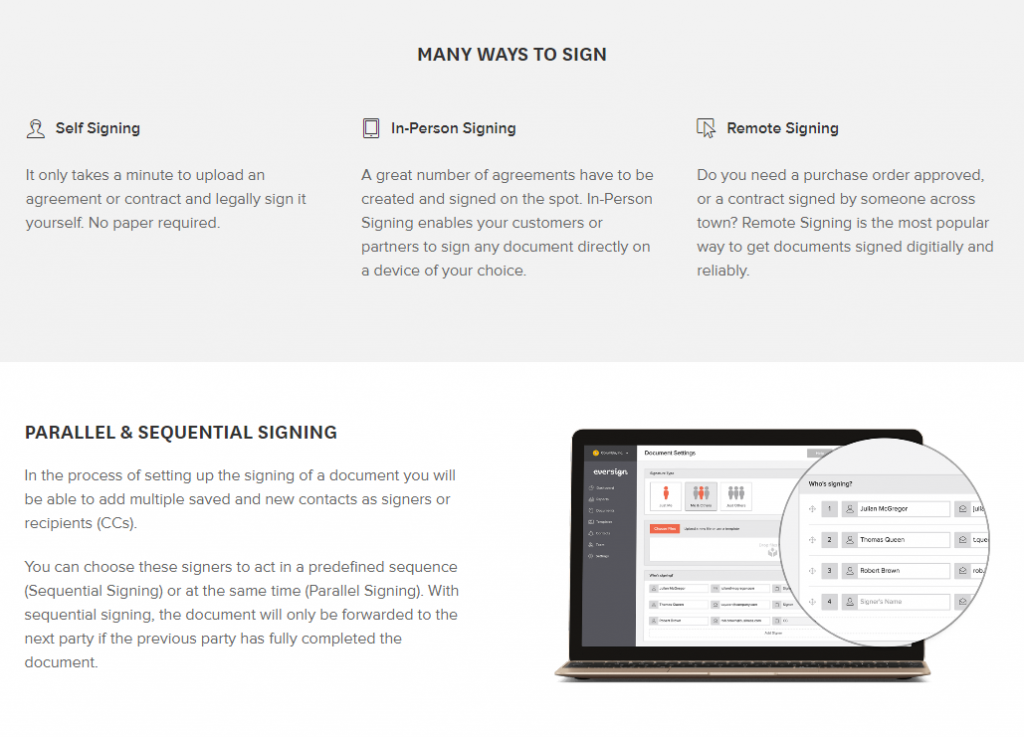
Eversign
Also offers free package (5 documents per month) and can be useful if sequential signing process is a requirement.
Learn more about the packages from Eversign at https://eversign.com/pricing
